Single Points of Failure (SPOF): Building Resilient Systems for the Future
#13 Don’t Put All Your Eggs in One Basket—How to Eliminate Single Points of Failure
Picture this: Your e-commerce platform is processing thousands of orders per minute during a flash sale—until a single database crashes, taking the entire system down. Customers rage, revenue plummets, and your brand takes a hit. This is the nightmare of a Single Point of Failure (SPOF). But what exactly is SPOF, and how can you avoid it? Let’s dive in.
Introduction
In the world of system design, reliability and scalability are non-negotiable. A Single Point of Failure (SPOF) is a critical vulnerability that can bring down an entire system, no matter how well-designed the rest of it is. Whether you’re building a small app or a large-scale enterprise platform, understanding and eliminating SPOFs is essential.
What is a Single Point of Failure?
A single point of failure is any part of a system that, if it fails, will cause the entire system to stop functioning.
Think of it as the weakest link in a chain—if it breaks, everything falls apart.
SPOFs can exist in hardware, software, or even processes.
Examples:
A single database server handling all user requests.
A lone power supply for a data center.
A payment gateway with no backup or failover mechanism.
Why it matters:
In today’s digital-first world, downtime is costly. A single failure can lead to lost revenue, damaged reputation, and frustrated users. Eliminating SPOFs ensures your system remains operational, even when things go wrong.
Why SPOF is Essential to Address?
SPOFs are not just technical issues—they are business risks. Consider the following scenarios:
Examples:
Case Study: Amazon’s 2018 Outage: In 2018, an AWS outage caused by a single misconfigured server disrupted services for millions of users, including major companies like Netflix and Slack. The financial impact was staggering.
Scenario: A social media app relies on a single authentication server. If it crashes, no one can log in, and the app becomes unusable.
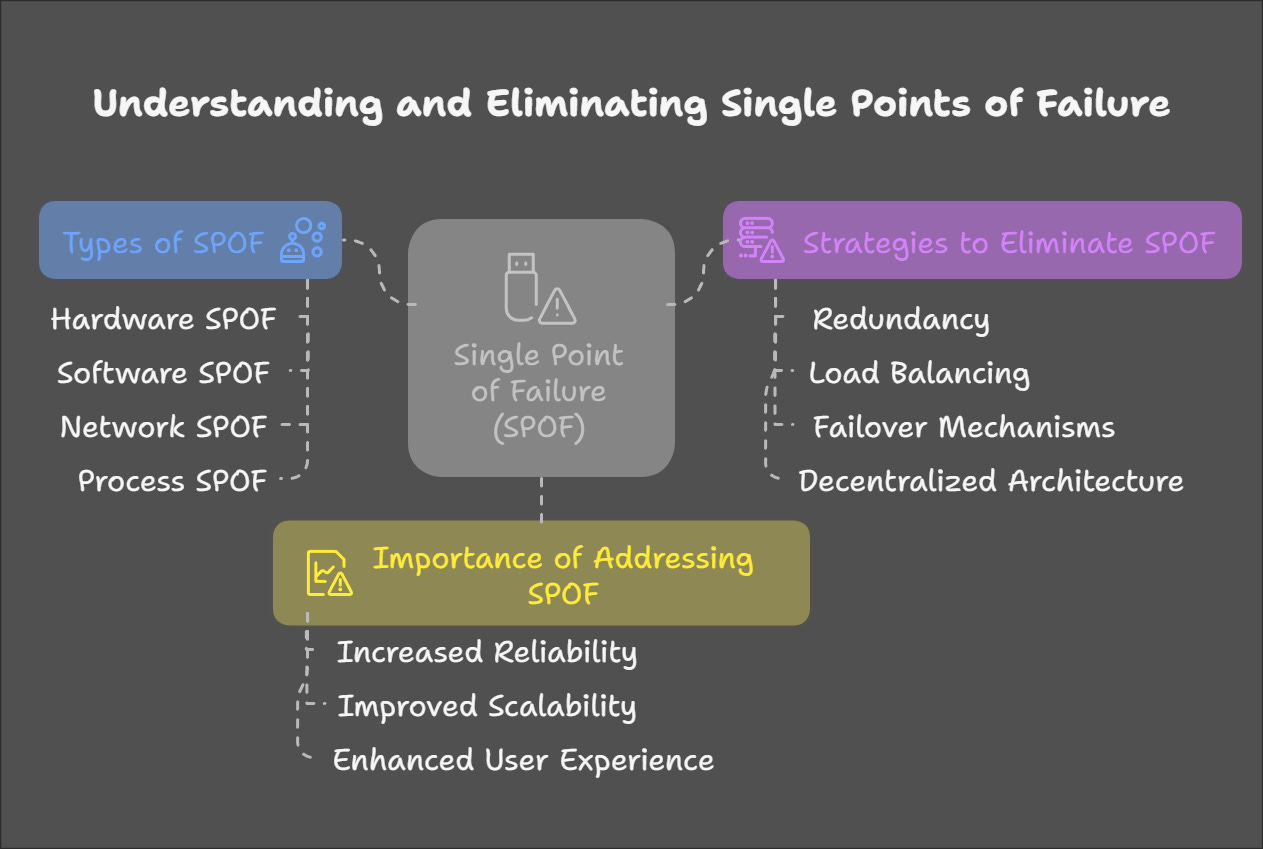
Benefits of Eliminating SPOFs:
Increased Reliability: Systems can handle failures gracefully without crashing.
Improved Scalability: Redundancy allows systems to scale horizontally.
Enhanced User Experience: Minimized downtime keeps users happy and engaged.
How Does Avoiding SPOF Work?
Avoiding SPOF involves designing systems with redundancy, failover mechanisms, and distributed architectures. The goal is to ensure that no single component is irreplaceable.
Examples:
A single server hosting your application.
A monolithic architecture where all services are tightly coupled.
Why it works:
When a system is designed without redundancy, the failure of one component disrupts the entire workflow. By introducing redundancy, load balancing, and failover mechanisms, systems can continue operating even if one part fails.
Types of SPOF in System Design
SPOFs can manifest in various forms. Here are the most common types:
Hardware SPOF:
Example: A single server hosting your database.
Solution: Use distributed databases or server clusters.
Software SPOF:
Example: A monolithic application where all services run on a single codebase.
Solution: Adopt microservices architecture to decouple services.
Network SPOF:
Example: A single router handling all network traffic.
Solution: Implement multiple network paths and failover routers.
Process SPOF:
Example: A manual deployment process that relies on one person.
Solution: Automate deployments and use CI/CD pipelines.
By addressing these types, you can build systems that are robust and resilient.
Strategies to Eliminate SPOF:
How to Kill SPOFs for Good:
Examples:
Redundancy: Use multiple instances of critical components (e.g., databases, servers).
Load Balancing: Distribute traffic evenly across servers to prevent overload.
Failover Mechanisms: Automatically switch to backup systems during failures.
Decentralized Architecture: Use microservices or distributed systems to isolate failures.
Tools to Help:
Cloud Services: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer built-in redundancy and failover options.
Monitoring Tools: Tools like Prometheus and Grafana can help detect and mitigate SPOFs in real-time.
Conclusion
SPOFs are silent killers—but with redundancy, failovers, and smart architecture, you can bulletproof your systems. By understanding what they are, why they matter, and how to eliminate them, you can design systems that are reliable, scalable, and resilient. Whether you’re a startup or a tech giant, addressing SPOFs should be a top priority.
Ready to build a failure-proof system? Share your thoughts or questions in the comments below, and let’s discuss how to eliminate SPOFs in your next project!
Thank You for Reading!
Loved this? Hit ❤️ to share the love and help others find it!
Get weekly tech insights to code smarter and build your dev career. Subscribe to CoreCraft for practical tips and frameworks you can use today.
Have ideas or questions? Drop a comment—I reply to all! For collabs or newsletter sponsorships, email me at souravb.1998@gmail.com
Stay connected: Follow me on X | LinkedIn | YouTube
P.S.
P.S. Slow apps killing your projects? Grab my Cache Rules Everything: A Developer’s Guide to Faster Applications for pro caching techniques that 10x speed. Get it now. Peek at my top 3 optimization hacks for more dev wins!
P.P.S.
Creators: Promote your tech work to my readers! Email souravb.1998@gmail.com for collab or sponsorship spots.