HTTP vs HTTPS: Why Website Security Matters
#14 Discover differences between HTTP and HTTPS, how encryption protects your data, and why every website needs SSL/TLS.
Did you know that 85% of users abandon a website if it’s labeled "Not Secure"? In an era of cyber threats, the difference between HTTP and HTTPS could mean the safety—or exposure—of your personal data.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the foundation of web communication— but it sends data in plain text, making it vulnerable.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) adds encryption via SSL/TLS, turning sensitive information into unreadable code.
Why HTTP Is Like Sending a Postcard (And HTTPS a Locked Safe):
✅ Security – Prevents hackers from stealing passwords, credit cards, and private info.
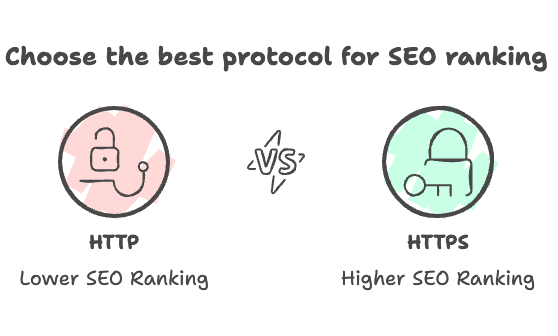
✅ Trust – Google ranks HTTPS sites higher and marks HTTP as Not Secure.
✅ Performance – HTTPS enables faster loading modern protocols like HTTP/2.
1. HTTP: The Backbone of the Web (But Is It Safe?)
What Is HTTP?
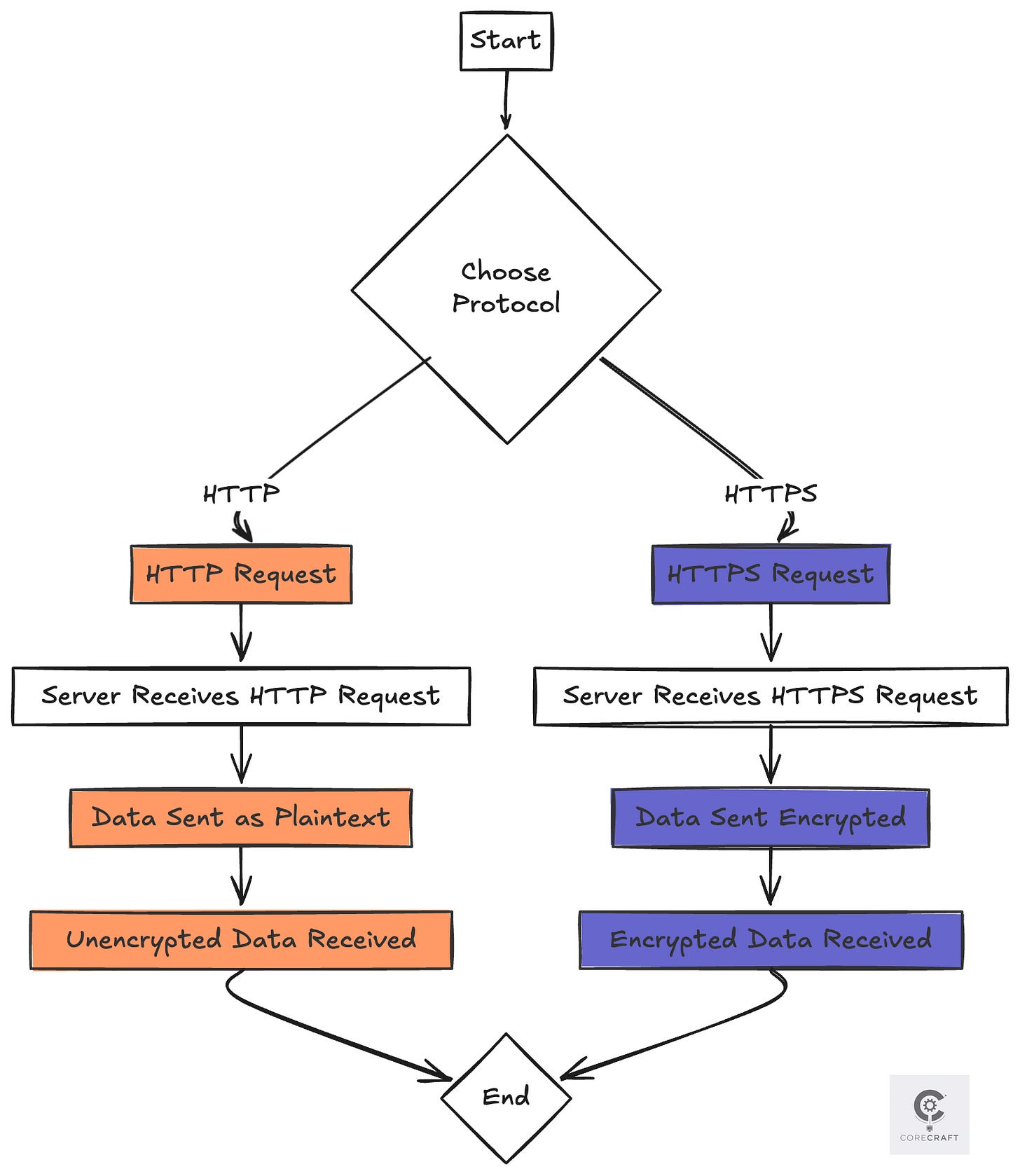
HTTP is the original protocol for sending and receiving web data. When you browse a site, your browser sends an HTTP request, and the server responds with the webpage.
Key Facts:
Operates on port 80.
Data is unencrypted (like sending a postcard anyone can read).
Uses status codes (e.g., 404 Not Found, 200 OK).
Example:
If you submit a login form over HTTP, hackers on the same network can intercept your username and password.
2. HTTPS: The Secure Alternative
What Is HTTPS?
HTTPS = HTTP + SSL/TLS encryption. It ensures that all data exchanged is scrambled, so only the intended recipient can decode it.
How It Works:
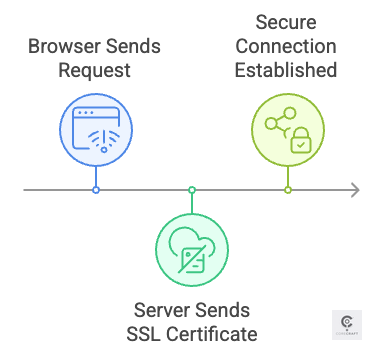
SSL/TLS Handshake – Your browser and server verify each other’s identity.
Encryption – Data is locked with a secure key before transmission.
Authentication – A padlock icon (🔒) confirms the site is legit.
Example:
Online banking requires HTTPS—otherwise, your transactions could be stolen.
3. SSL/TLS Certificates: The Trust Behind HTTPS
Why Do You Need an SSL Certificate?
Proves your website’s identity (no impersonation).
Enables encryption (turns data into unbreakable code).
Boosts Google rankings (SEO benefit).
Where to Get One:
✔ Free: Let’s Encrypt, Cloudflare.
✔ Paid: DigiCert, Comodo, eMudhra.
Browser Warning:
🚨 If a site has an invalid certificate, Chrome/Firefox will block access.
4. HTTP vs HTTPS: Key Differences Compared
Security → HTTP: ❌ No encryption | HTTPS: ✅ Encrypted (SSL/TLS)
Port → HTTP: 80 | HTTPS: 443
Speed → HTTP: Slower | HTTPS: Faster (supports HTTP/2)
SEO → HTTP: Lower ranking | HTTPS: Google prefers it
Trust → HTTP: "Not Secure" warning | HTTPS: Padlock (🔒)
Use Case → HTTP: Basic sites | HTTPS: Must for logins/payments
HTTPS is the secure, faster, and SEO-friendly choice. 🚀
5. Why You Must Switch to HTTPS (6 Key Benefits)
Stops Data Theft – Encrypts login details, payments, and personal info.
Boosts SEO – Google prefers HTTPS sites in search rankings.
Builds Trust – 92% of users check for the padlock before buying.
Improves Speed – HTTPS supports HTTP/2, making pages load faster.
Secure Referrals – Analytics track traffic sources more accurately.
Future-Proofing – Browsers (Chrome, Firefox) now block HTTP sites.
Conclusion: HTTPS Is No Longer Optional
The web is moving toward 100% HTTPS. If your site still uses HTTP, you’re:
Losing traffic (users avoid "Not Secure" warnings).
Missing SEO gains (Google favors HTTPS).
Risking data breaches (unencrypted = easy target).
🚀 Ready to Secure Your Site? Check your SSL status now with SSL Labs Test.
Thank You for Reading!
Loved this? Hit ❤️ to share the love and help others find it!
Get weekly tech insights to code smarter and build your dev career. Subscribe to CoreCraft for practical tips and frameworks you can use today.
Have ideas or questions? Drop a comment—I reply to all! For collabs or newsletter sponsorships, email me at souravb.1998@gmail.com
Stay connected: Follow me on X | LinkedIn | YouTube
P.S.
P.S. Slow apps killing your projects? Grab my Cache Rules Everything: A Developer’s Guide to Faster Applications for pro caching techniques that 10x speed. Get it now. Peek at my top 3 optimization hacks for more dev wins!
P.P.S.
Creators: Promote your tech work to my readers! Email souravb.1998@gmail.com for collab or sponsorship spots.